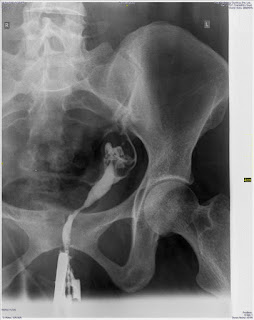
Haglund Syndrome with Normal Os Peroneum
A female patient with pain in the posterior aspect of the heel-
 |
| Os peroneum is normally located lateral to the cuboid. Accesory Navicular is also noted |
 |
| Thickening of Achilis tendon at its insertion with enthesophyte and adjacent soft tissue swelling. There is mild loss of normal retro-calcaneal luceny s/o retro-calcaneal bursitis |
Haglund Syndrome:
It is said to be present in cases of patients with heel pain if following signs are present-
- Achillis insertional site enthesophytes.
- Insertional Achillis tendinitis,
- Retro-calcaneal( Kager's fat) and Retro-achillis bursitis.
- Bone marrow edema in calcaneal tuberosity( MRI)
Predisposing factors: Hind foot varus and pes cavus.
Those wearing low back shoes are prone for HS-
Os Peroneum:
Located adjacent to calcaneo-cuboid joint( lateral radiograph- 7mm proximal -8mm distal to CC joint, Oblique radiograph- .9mm proximal and 8mm distal to CC jt)
It lies within the peroneus longus tendon.
It can be uni-partite/bi-partite or multi-partite( margins have to be well defined and corticated with minimal i.e. less than 2mm inter-fragment distance).
Fracture of Os Peroneum- os peroneum fragment separation of 6 mm or more or displacement of the proximal Os peroneum fragment by
10 mm or more proximal to the calcaneocuboid joint on a
lateral radiograph or by 20 mm or more proximal to the calcaneocuboid joint on an
oblique radiograph. It is associated with full-thickness tear of the peroneus longus tendon.
Heel Pain Causes:
The most common causes of heel pain are plantar fasciitis (bottom of the heel) and Achilles tendinitis (back of the heel).
Differential Diagnosis Considerations:
Arthritic -Gout, rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative arthropathy; primary or secondary
osteoarthritis
Infectious -Diabetic ulcer, osteomyelitis, plantar warts
Mechanical
Plantar—
plantar fasciitis, heel spur, calcaneal stress fracture, medial or lateral
plantar nerve entrapment, heel pad syndrome, foreign body granulomatosis
Posterior—
Achilles tendinopathy, Haglund deformity, retrocalcaneal bursitis, tarsal
coalition, accessory muscles( accesory soleus muscle in posteromedial heel pain), Sever disease (pediatrics)
Neuropathic- Lumbar radiculopathy, nerve entrapment, neuroma, tarsal tunnel syndrome
Trauma
Tumor (rare) -Ewing sarcoma, neuroma
Vascular (rare)